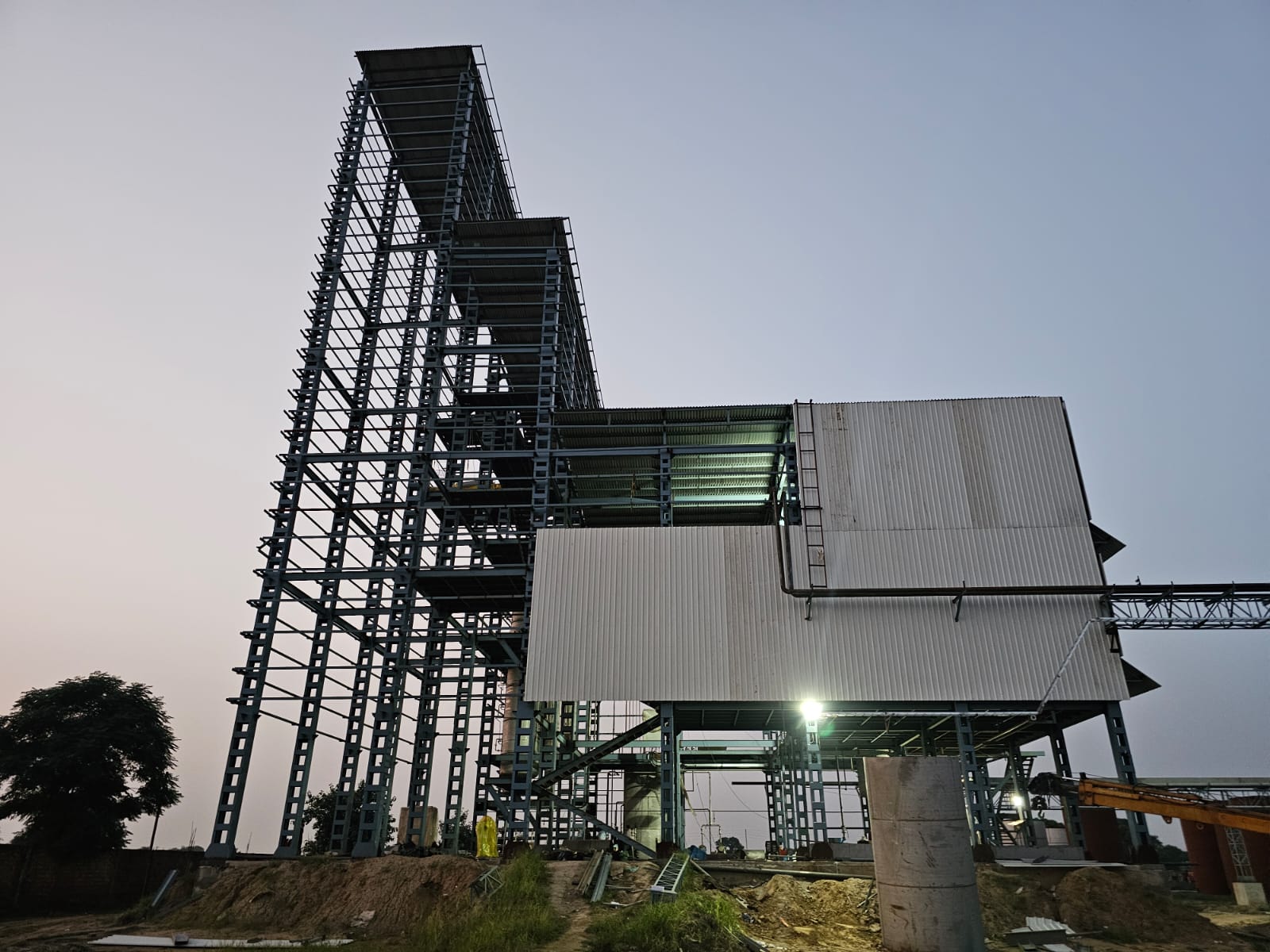
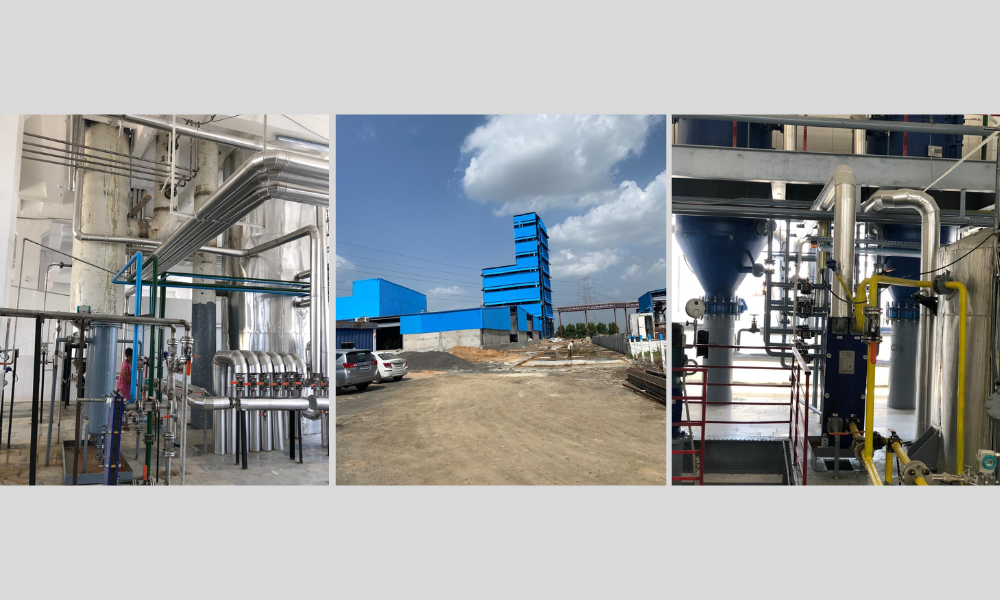
The process of refining is divided into a number of major steps that refine and stabilize the oil. The entire stages of refining, starting with crude oil, to the final package are as follows.
Pre-treatment
Pre-treatment is a process of refining crude oil by eliminating coarse impurities and water that are to be subjected to downstream refining. This entails rough filtration to eliminate particulates and regulated heating to dry up the moisture. Pre-filtration will minimize the load on degumming and bleaching units and give a clear final oil.
Degumming
Degumming acts on phospholipids (gums), which make the water turbid and decrease shelf life. This can be done by water degumming (with hydration phospholipids), acid degumming (with non-hydrated phospholipids), and enzymatic degumming with phospholipase. Proper degumming lowers the levels of phosphorus to acceptable levels and stabilizes the oil to be bleached. The equipment usually involves mixers, reactors, and centrifugal separators to isolate hydrated gums.
Neutralization (Chemical Refining)
In the case of chemical refining, caustic soda (NaOH) is added to neutralize the presence of free fatty acids (FFA) to form soap stock. In order to prevent excessive loss of oil, controlled dosing, temperature regulation (typically 80-85°C), and effective mixing are necessary. After the reaction, centrifugation is used to separate soap stock and neutral oil. Soap stock is a useful by-product that can be used in the manufacture of Soap or in the production of acid oil. The quality of the soap stock determines the economics of downstream processing.
Water Washing
The neutralization is followed by washing with hot, soft water to remove alkali and soaps. Several steps of washing can be applied, and each is preceded by centrifugation. The water-to-oil ratios and temperature (usually around 95 °C) will take care of keeping the soap content under the target ppm to avoid the formation of off-flavors and foaming during subsequent stages.
Vacuum Drying
Wet oil should be dried to prevent oxidation and to be ready to be bleached. Vacuum drying efficiently removes entrained moisture at low temperature to cause less thermal damage. The usual vacuum pressure and residence time are chosen so as to get moisture below 0.1 percent and retain the oil quality.
Bleaching
Bleaching is the process of removing pigments (chlorophyll, carotenoids), trace metals, and leftover gums with the help of activated bleaching earth (clays) or carbon. This is carried out at high temperature (95-105°C) and under vacuum to preserve oil. The modern systems involve automated dosing of bleaching earth, multi-stage contactors to enhance optimization of residence, and spent earth recovery systems. Improved oil color, off-note reduction, and preparation of oil to final polishing can be achieved with effective bleaching.
Filtration
After the bleach stage, filters (pressure leaf filters or filter presses) are used to remove spent earth and fine particles. The filtration process is an important procedure to obtain the required level of clarity and to safeguard the deodorizer packing and polishing filters in the downstream. Filter design should be such that it enables easy discharge and cleaning of cakes to reduce downtime.
Dewaxing / Winterization
Dewaxing or winterization is done to oils that crystallize at low temperatures (sunflower, rice bran, corn). This involves cooling under control to crystallize the waxes, stirring to promote uniform crystal growth, and filtering off or spinning off the wax crystals. The procedure guarantees the oil to be in a clear condition at refrigeration temperatures, besides producing food-grade wax as a possible by-product.
Deodorization (Final Step)
Deodorization involves the treatment of volatile odorous compounds and leftover FFAs with the help of high-temperature (usually, 240-260 °C) steam that strips away these volatile substances under high vacuum. Mass transfer is enhanced through structured packing or efficient stripping internals. Important parameters are retention time (45 -75 minutes) and the vacuum level. When controlled well, the deodorization process produces a light-colored, tasteless oil that has low amounts of FFA.
Fatty Acid Recovery
Volatile fractions and distillates are used and processed to extract valuable substances such as tocopherols, squalene, and fatty acids. These are commercial feedstocks to the soap, cosmetics, or biofuel industries and components of a zero-waste strategy.
Final Processing
The oil is then deodorized, followed by the addition of antioxidants and vitamin fortificants (where necessary) under controlled conditions, and finally, polishing filtration is done to bring the oil to package standards. The finished oil is then pumped to storage tanks or the packing line.